Understanding On-Chain vs Off-Chain Transactions: A Beginner’s Guide
Summary
Introduction: On-Chain vs Off-Chain Transactions
In the world of cryptocurrency, understanding the mechanisms behind transactions is crucial. Two primary types of transactions exist: On-Chain vs Off-Chain Transactions. Each method has its unique characteristics, advantages, and limitations. This guide aims to demystify these concepts, providing clarity on how each works and when to use them.
What Are On-Chain Transactions?
On-chain transactions are those that occur directly on the blockchain. When you initiate an on-chain transaction, it is broadcast to the network, validated by nodes, and then added to the blockchain ledger. This process ensures transparency and security but can be time-consuming and costly.
Key Characteristics:
- Transparency: Transactions are publicly recorded on the blockchain.
- Security: Validation through consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work or Proof of Stake.
- Immutability: Once confirmed, transactions cannot be altered or reversed.
- Cost: Transaction fees can be high, especially during network congestion.
Ideal Use Cases:
- Large Asset Transfers: Suitable for significant asset transfers where security is paramount.
- Smart Contracts: Execution of decentralized applications requiring transparency and trustlessness.
- Regulatory Compliance: Situations where an immutable record is necessary for compliance purposes.
What Are Off-Chain Transactions?
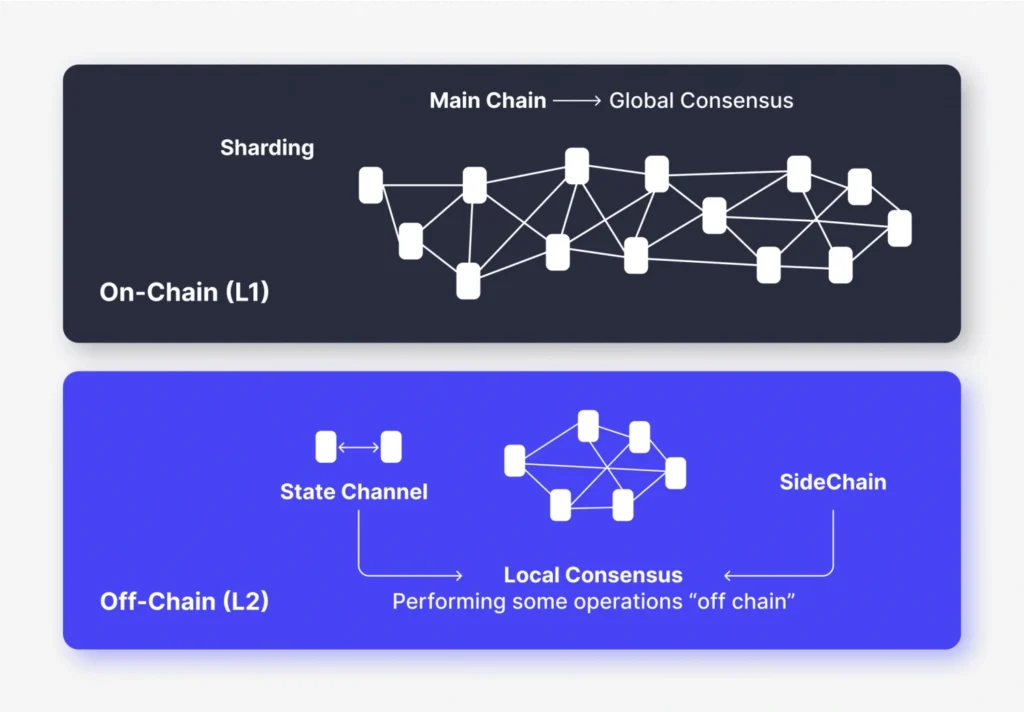
Credit from B2BinPay
Off-chain transactions take place outside the main blockchain network. These transactions are not immediately recorded on the blockchain but may be later settled or recorded through secondary channels or layer-2 solutions. Off-chain methods aim to improve scalability and reduce costs.
Key Characteristics:
- Speed: Transactions can be processed quickly without waiting for blockchain validation.
- Cost: Lower transaction fees due to reduced computational requirements.
- Privacy: Enhanced privacy as transaction details may not be immediately recorded on the blockchain.
- Security: Potentially less secure, depending on the off-chain solution used.
Ideal Use Cases:
- Microtransactions: Small-value transactions that would be uneconomical on-chain due to high fees.
- Gaming and NFTs: In-game purchases and non-fungible token (NFT) transfers that benefit from reduced transaction times and costs.
- Layer-2 Solutions: Implementations like the Lightning Network for Bitcoin or Optimistic Rollups for Ethereum that facilitate off-chain transactions.
Comparing On-Chain and Off-Chain Transactions
| Feature | On-Chain Transactions | Off-Chain Transactions |
|---|---|---|
| Transparency | Fully transparent | Limited transparency |
| Security | High (due to blockchain validation) | Variable (depends on off-chain method) |
| Speed | Slower due to network consensus | Faster |
| Cost | Higher transaction fees | Lower transaction fees |
| Immutability | Transactions are permanent | May be subject to change or reversal |
| Scalability | Limited by blockchain capacity | Higher, as transactions are processed off-chain |
When to Use On-Chain Transactions
Opt for on-chain transactions when:
- Security is a Priority: When transferring significant amounts of cryptocurrency or assets where security is a top concern.
- Transparency is Required: Situations where a transparent and auditable record is necessary.
- Regulatory Compliance: Scenarios that require an immutable and publicly accessible record for compliance purposes.
When to Use Off-Chain Transactions
Consider off-chain transactions when:
- Speed is Essential: For quick transfers, especially in trading or gaming environments.
- Cost Efficiency is Important: When dealing with small-value transactions where on-chain fees would be prohibitive.
- Privacy is a Concern: When transaction details should not be immediately recorded on the blockchain.
Conclusion
Credit from ZebPay
Understanding the differences between on-chain and off-chain transactions is essential for navigating the cryptocurrency landscape. On-chain transactions offer unparalleled security and transparency, making them suitable for high-value and compliance-sensitive applications. Conversely, off-chain transactions provide speed and cost efficiency, catering to scenarios where these factors are prioritized. By evaluating the specific requirements of each use case, individuals and businesses can make informed decisions on the appropriate transaction method to employ.




